German Research Foundation (DFG)

Elektromagnetische Sensoren für Life Sciences (ESSENCE)
Priority Programme - SPP 1857
Support Code: DFG PF 661/7-1
Project Initiator:
Pfeiffer, Ullrich, Prof. Dr. rer. nat.
High Frequency Systems in Communications Technology / Terahertz-Technology, Automotive Radar Systems
Bergische Universität Wuppertal
Zimmer, Thomas, Prof. Dr.
Universität Bordeaux
Macgrogan, Gaetan, Dr.
Unicancer Group Bordeaux
Project Objectives:
The NearSense project has the challenging objective to propose a fully integrated all-electronic silicon based sensor for medical and biological applications, which is low-cost, handheld, small, and additionally able to work at room-temperature. NearSense requires major innovations in an inter-disciplinary research field and is therefore conducted by an interdisciplinary team who will jointly identify the relevant bio imaging parameters for marker-free intraoperative tumor margin identification in tissue sample tests and blind tests.
Informations
Project duration:
Aug 2015 - Dec 2018
Funding:
German Research Foundation (DFG)
Tags
Histology, tumor margin identification, intraoperative, terahertz waves, sub-wavelength resolution, ex-vivo medical imaging, near-field sensor array, silicon technology
Second project phase
A silicon-based terahertz near-field imaging array for ex vivo life-science applications - Phase 2 Support Code: DFG PF 661/7-2
Project Objectives:
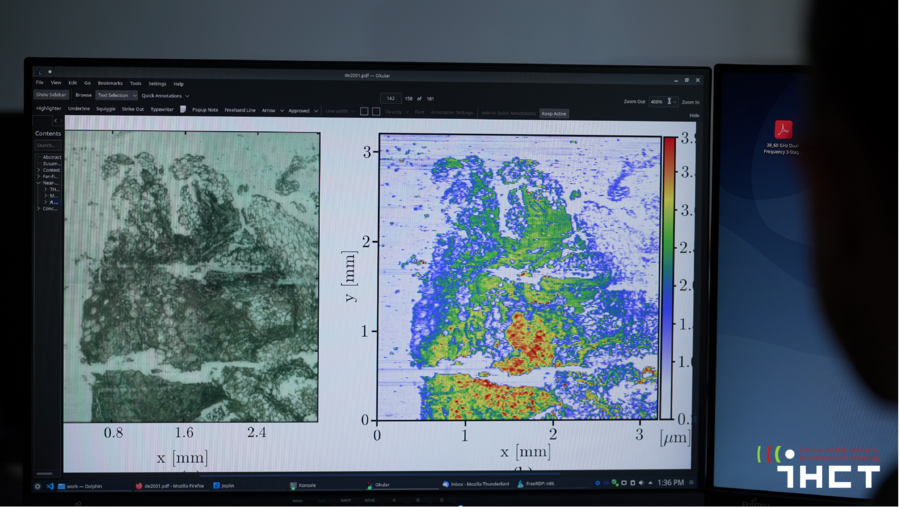
The project's main objective is to leverage silicon-based economies-of-scale for a technology breakthrough in life-science. The aim is to develop a silicon-based THz sub-wavelength imager for tumor margin identification and the results of this interdisciplinary research proposal will help a surgeon to make an instantaneous (intraoperative) decision during an oncological surgery - substantially improving the quality-of-life of a patient. The challenging objective of NearSense requires major innovations in an inter-disciplinary research field. The NearSense research is, therefore, conducted by an interdisciplinary team of physicists, oncologic surgeons, histopathologists and engineers. The scientific breakthrough in the first phase was achieved by a fully-integrated THz near-field sensor pixel comprising of a THz source (transmitter), an electromagnetic near-field sensor element (transducer), a THz detector (receiver) including the readout thereof. The THz near-field sensor pixel provided the dielectric properties (complex permittivity) of bio cells on the micrometer scale. The projects second phase leverages silicon-technologies to integrate large 2-D arrays with real-time acquisition capability to provide a surgeon with high resolution THz video analysis during an oncological surgery. NearSense exploits the benefits of the terahertz radiation with the required sub-wavelength optical resolution for intraoperative bio imaging without the need for scanning.
Informations
Project duration:
Oct 2018 - Dec 2021
Funding:
German Research Foundation (DFG)
Tags
flexible RF electronics, metal-oxide TFT, wireless communication, circuit design
